The recent addition of dropreason.h in Linux 6+ kernels provides detailed reasons for packet drops. The netlink drop_monitor API has been extended to include the NET_DM_ATTR_REASON attribute to report the drop reason, see net_dropmon.h.
The following example illustrates the value of the reason code in explaining Linux packet drops.
tcp_v4_rcv+0x7c/0xef0The value of NET_DM_ATTR_SYMBOL shown above indicates that the packet was dropped in the tcp_v4_rcv function in Linux kernel at memory location 0x7c/0xef0. While this information is helpful, there are many reasons why a TCP packet may be dropped.
NO_SOCKETIn this case, the value of NET_DM_ATTR_REASON shown above indicates that the TCP packet was dropped because no application had opened a socket and so there was nowhere to deliver the packet.
In the case of Linux-based hardware switches or smart network adapters, where packet processing is offloaded to hardware, the netlink drop_monitor events include NET_DM_ATTR_HW_TRAP_GROUP_NAME and NET_DM_ATTR_HW_TRAP_NAME attributes and packet header information supplied by the hardware driver, see Devlink Trap.
The latest version of the open source Host sFlow agent includes adds support for the NET_DM_ATTR_REASON attribute to improve the accuracy of the sFlow drop_reason.
port_unreachableIn our example, the Host sFlow is now able to report port_unreachable as the reason for the dropped packet, rather than a generic unknown_l4 reason reported for older kernels.
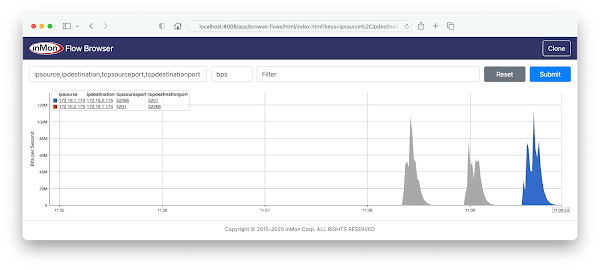
The screen capture at the top of this article shows dropped packet information displayed in real-time using the Discard Browser application running on the sFlow-RT analytics engine. The chart demonstrates how the combination of information from the header of the dropped packet along with the reason for dropping the packet quickly gets to the root cause of the packet drop. In this case an attempt has been made from 172.16.1.174 to connect to 172.16.1.1 via telnet (tcp port 23) and telnet has not been enabled on the server so the packet was dropped - as it should be since telnet is not a secure method of connecting.
docker run --name sflow-rt -p 8008:8008 -p 6343:6343/udp -d sflow/prometheus
A quick way to experiment with sFlow is to run the pre-built sflow/prometheus image using Docker. The bundled Discard Browser with the settings shown in the screen capture can be launched by clicking here.