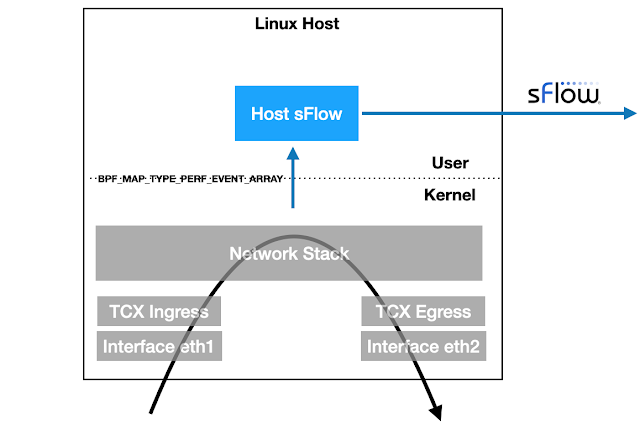
Linux 6.11+ kernels provide TCX attachment points for eBPF programs to efficiently examine packets as they ingress and egress the host. The latest version of the open source Host sFlow agent includes support for TCX packet sampling to stream industry standard sFlow telemetry to a central collector for network wide visibility, e.g. Deploy real-time network dashboards using Docker compose describes how to quickly set up a Prometheus database and use Grafana to build network dashboards.
static __always_inline void sample_packet(struct __sk_buff *skb, __u8 direction) {
__u32 key = skb->ifindex;
__u32 *rate = bpf_map_lookup_elem(&sampling, &key);
if (!rate || (*rate > 0 && bpf_get_prandom_u32() % *rate != 0))
return;
struct packet_event_t pkt = {};
pkt.timestamp = bpf_ktime_get_ns();
pkt.ifindex = skb->ifindex;
pkt.sampling_rate = *rate;
pkt.ingress_ifindex = skb->ingress_ifindex;
pkt.routed_ifindex = direction ? 0 : get_route(skb);
pkt.pkt_len = skb->len;
pkt.direction = direction;
__u32 hdr_len = skb->len < MAX_PKT_HDR_LEN ? skb->len : MAX_PKT_HDR_LEN;
if (hdr_len > 0 && bpf_skb_load_bytes(skb, 0, pkt.hdr, hdr_len) < 0)
return;
bpf_perf_event_output(skb, &events, BPF_F_CURRENT_CPU, &pkt, sizeof(pkt));
}
SEC("tcx/ingress")
int tcx_ingress(struct __sk_buff *skb) {
sample_packet(skb, 0);
return TCX_NEXT;
}
SEC("tcx/egress")
int tcx_egress(struct __sk_buff *skb) {
sample_packet(skb, 1);
return TCX_NEXT;
}
The sample.bpf.c file is compiled into eBPF code that the Host sFlow mod_epcap.c module uses to tap packets on selected interfaces. The highlighted code uses the bpf_get_random_u32() function to randomly select packets using the configured sampling rate for the interface. Once a packet is selected to be sampled, the packet header and selected metadata is captured and sent to the Host sFlow agent as a performance event via the bpf_perf_event_output() call. The ability to perform the sampling action in the kernel dramatically reduces the overhead associated with network traffic monitoring, since only the small fraction of sampled packets need to be transferred to the user space Host sFlow agent.
static __always_inline __u32 get_route(struct __sk_buff *skb) {
__u32 key = 0;
__u32 *routing_enabled = bpf_map_lookup_elem(&routing, &key);
if(!routing_enabled || !*routing_enabled)
return 0;
if(skb->pkt_type != PACKET_HOST)
return 0;
void *data = (void *)(long)skb->data;
void *data_end = (void *)(long)skb->data_end;
struct ethhdr *eth = data;
if ((void *)(eth + 1) > data_end)
return 0;
__u32 proto = bpf_ntohs(eth->h_proto);
if(proto == ETH_P_IP) {
struct iphdr *ip = data + sizeof(*eth);
if ((void *)(ip + 1) > data_end)
return 0;
struct bpf_fib_lookup fib = {0};
fib.family = AF_INET;
fib.ipv4_src = ip->saddr;
fib.ipv4_dst = ip->daddr;
fib.tos = ip->tos;
fib.l4_protocol = ip->protocol;
fib.sport = 0;
fib.dport = 0;
fib.tot_len = bpf_ntohs(ip->tot_len);
fib.ifindex = skb->ifindex;
long rc = bpf_fib_lookup(skb, &fib, sizeof(fib), 0);
if(rc != BPF_FIB_LKUP_RET_SUCCESS)
return 0;
return fib.ifindex;
} else if(proto == ETH_P_IPV6) {
struct ipv6hdr *ipv6 = data + sizeof(*eth);
if ((void *)(ipv6 + 1) > data_end)
return 0;
struct bpf_fib_lookup fib = {0};
fib.family = AF_INET6;
__builtin_memcpy(fib.ipv6_src, &ipv6->saddr, sizeof(ipv6->saddr));
__builtin_memcpy(fib.ipv6_dst, &ipv6->daddr, sizeof(ipv6->daddr));
fib.flowinfo = *(__be32 *) ipv6 & bpf_htonl(0x0FFFFFFF);
fib.l4_protocol = ipv6->nexthdr;
fib.sport = 0;
fib.dport = 0;
fib.tot_len = bpf_ntohs(ipv6->payload_len);
fib.ifindex = skb->ifindex;
long rc = bpf_fib_lookup(skb, &fib, sizeof(fib), 0);
if(rc != BPF_FIB_LKUP_RET_SUCCESS)
return 0;
return fib.ifindex;
}
return 0;
}
If the Linux host has been configured as a router, then the bpf_fib_lookup() is used to to determine the forwarding decision (egress port) for sampled ingress packets.
Note: The mod_pcap.c module works on older Linux kernels and uses traditional BPF to perform random packet sampling. The main advantage of the mod_epcap module is its ability add additional metadata to each sampled packet.

No comments:
Post a Comment